Iliotibial Band Syndrome
Check out our updated post on IT band treatment found here: New Methods in Treating IT Band Syndrome!
Iliotibial band syndrome (ITBS) is a painful, frustrating condition that affects the outside part of the knee. The IT band is a thickening of inelastic connective tissue which arises from the Tensor Fascia Latae and the Gluteal muscles and inserts into the outside of the tibia and Tibialis Anterior.1 During movement, the IT band approximates the lateral aspect of the knee, creating an “impingement zone” and irritates the tissues found there, primarily a highly innervated fat pad.2,5 With repetitive flexion and extension of the knee, particularly during excessive running, ITBS can develop and cause moderate to severe pain on the outside of the knee.
Who is at risk?
Active individuals are prone to iliotibial band syndrome due to chronic “overuse” type of trauma to the IT band and muscles of the thigh/buttock. A number of risk factors put a person at a greater risk for developing ITBS which include: training intensity/duration, running down hills, wearing shoes with poor arch support, biomechanical factors such as flat feet, gluteus medius weakness, etc.4 Runners who run while fatigued, may be at more of a risk for developing ITBS due to increased flexion at foot-strike; this results in greater impingement at the “impingement zone” of the knee leading to greater tissue irritation.2
Examination
Sports chiropractors will carefully evaluate the knee including: ROM, various orthopedic tests, and a specific palpatory assessment, which allows the practitioner to identify muscles that have developed myofascial adhesions, causing muscle tension and pain.
The knee is caught between two other main joints of the lower extremity: the ankle, and the hip. The IT band connects to the hip musculature and also has fascial connections to the tibialis anterior, the bulky muscle in the front of the lower leg.1 Examination of the hip, lower leg, and ankle may also be assessed in an attempt to determine dysfunctional muscles, joints, and structures which may be causing excessive stress at the outside of the knee.
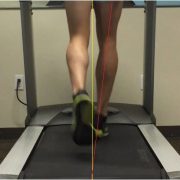
A functional evaluation will also be performed to determine movement patterns that may cause excessive stress on the knee/IT band. A gait assessment both walking and running may reveal over pronation at the foot, or hip dropping during the stance phase of the gait cycle. Squats and lunges may reveal deviation of the knee towards midline, which may indicate glute medius weakness on the same side.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the stage at which the ITBS is found at the time of examination. To combat swelling and pain associated with ITBS, treatment primarily involves ice and modification of activity.3,4 Patients can ice the knee at home using ice massage for 3-8 minutes, two times per day to combat the inflammatory process.
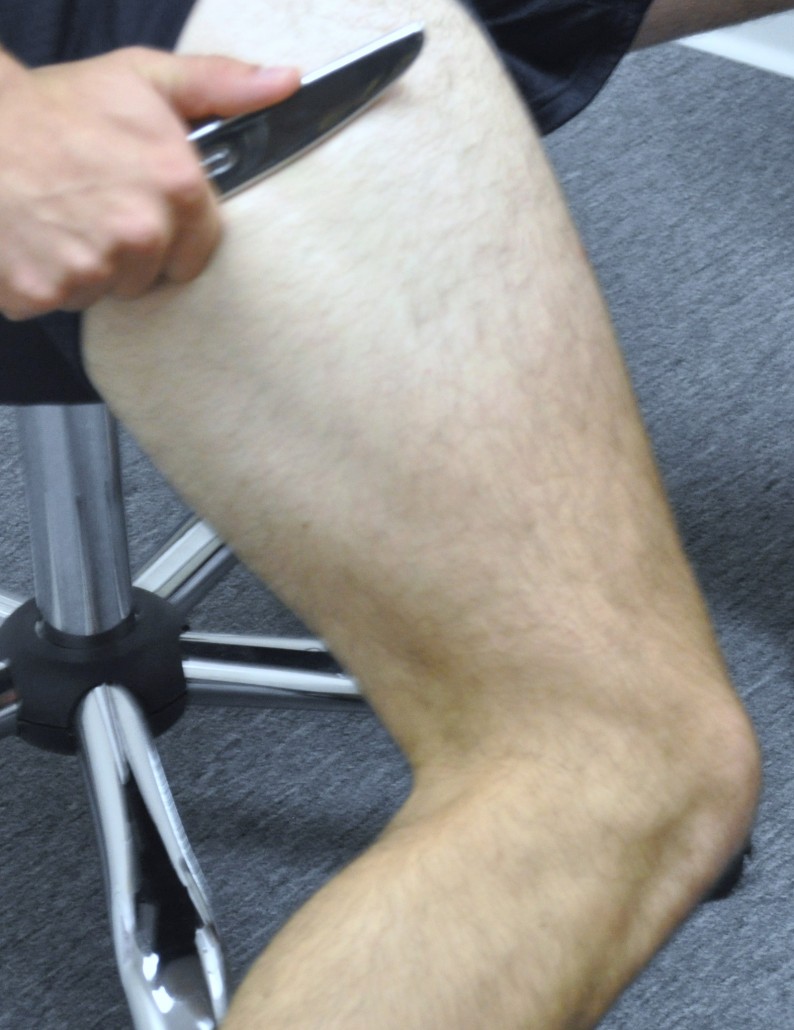
Sports chiropractic care primarily involves addressing the soft tissue structures that affect the IT band. Active Release Technique (ART®) is used to remove myofascial adhesions (scar tissue) that have developed in the muscles that surround or connect into the IT band: gluteus maximus/medius, TFL, vastus lateralis (outside quadriceps muscle), biceps femoris (outside hamstring), and in some cases the tibialis anterior. The practitioner will have you perform specific movements for each structure involved, while deep pressure is applied to the structure to help stretch the myofascial adhesions to help restore proper function to the muscles and remove excessive tension that may be exacerbating the ITBS.
Some ART® protocols are designed to break down adhesions within the muscles, while other protocols are designed to restore relative motion between myofascial structures. The latter is important for IT band syndrome as the band itself lies over the large vastus lateralis and biceps femoris. Improving the movement between these structures will help remove tension at the outside of the knee.
Chiropractic adjustments may be used to improve the joint function of the low back, pelvis, hip, knee, and ankle to help improve the symptoms at the knee.
Rehabilitation
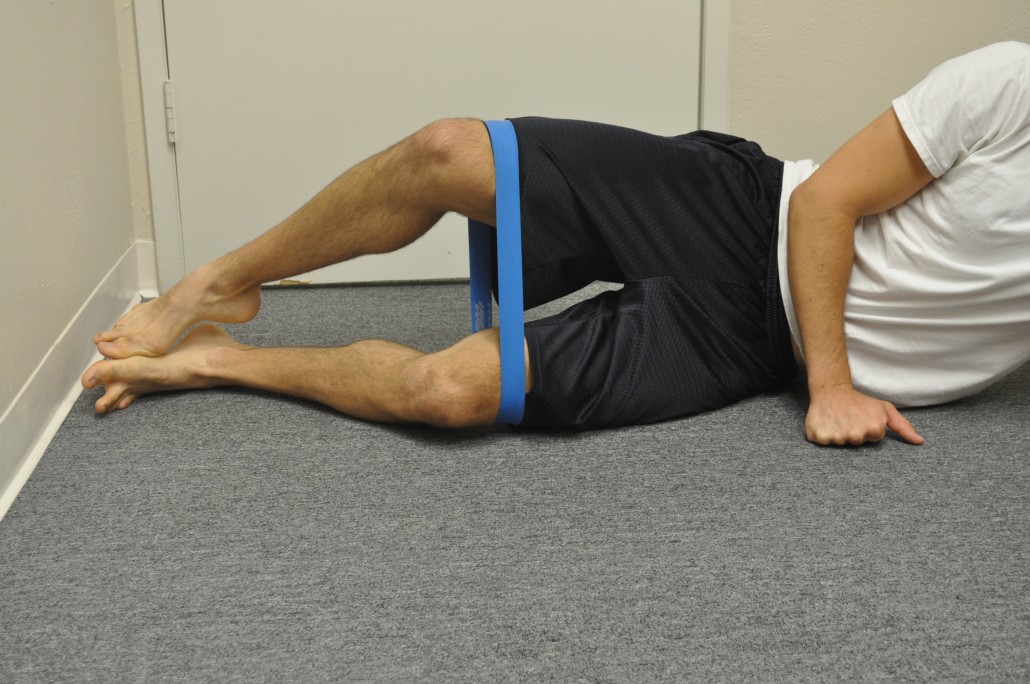
Once pain has significantly decreased, specific exercise protocols will be given to help prevent recurrence of symptoms and strengthen weak muscles such as the gluteus medius muscle. Gluteus medius weakness results in greater adduction angle at the knee (knee moves inward) during gait which results in over stabilization of the IT band leading to ITBS, trigger points, and contracted muscles.6,7 Proper strengthening of the glute medius will result in greater hip stabilization and keep the knee from deviating towards midline during dynamic movements (running, squatting, jumping).The IT band is an inflexible structure, however, IT band stretching can help relieve tension in the muscles that insert into the IT band. In addition to static stretching, the use of ischemic compression through the use of a foam roller can be used to successfully decrease the sensitivity and intensity of trigger points.8
For runners, once pain has been minimal for 2 weeks and strengthening exercises are performed, a running routine can resume.3,4 Running should take place every other day on a flat surface with easy sprints and no hills.3,4 Gradual increases in frequency and duration of running should occur over a period for 3 to 4 weeks.4
Other Treatment Options
Other treatment options for ITBS include NSAIDs for pain and swelling.4 In chronic cases that have not responded to conservative care, corticosteroid injections may be warranted.10 In rare cases surgery may be performed to release the tension of the IT band over the lateral knee.11
Conclusion
If you are experiencing knee pain, it is important to get evaluated by a sports chiropractor to determine the exact cause. ITBS is a very common condition affecting approximately 8.4% of injured runners.9There are a number of conservative options for patients who are affected with this condition, particularly Active Release Technique (ART®) to help relieve pain associated with ITBS. ART®, chiropractic adjustments, stretching of the TFL/IT band, followed by gluteus medius strengthening and a gradual return to activity will result in most patients recovering from ITBS in 6 weeks.4
References
Meyers, T. W. (2009) Anatomy Trains: Myofascial Meridians for Manual and Movement Therapists. New York, NY: Elsevier.
Fredericson, M., and Weir, A. (2006). Practical management of iliotibial band friction syndrome in runners. Clinical Journal of Sports Medicine, 16 (3), 261-268.
Ellis, R., Hing, W., and Reid, D. (2007). Iliotibial band friction syndrome- a systematic review. Manual Therapy, 12, 200-208.
Fredericson, M., Wolf, C. (2005). Iliotibial band syndrome in runners innovations in treatment. Sports Medicine, 35 (5), 451-459.
Fairclough, J. et al. (2006). The functional anatomy of the iliotibial band during flexion and extension of the knee: implications for understanding iliotibial band syndrome. Jounral of Anatomy, 208, 309-316.
Miller, R. H., Lowry, J. L., Meardon, S. A., and Gillette, J. C. (2006). Lower extremity mechanics of iliotibial band syndrome during an exhaustive run. Gait and Posture, 26, 407-413.
Ferber, R., Noehren, B., Hamill, J., and Davis, I. (2010). Competitive female runners with a history of iliotibial band syndrome demonstrate atypical hip and knee kinematics. Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy, 40 (2), 52-58.
Hanten, W. P., Olson, S. L., Butts, N. L., and Nowicki, A. L. (2000). Effectiveness of a home program of ischemic pressure followed by sustained stretch for treatment of myofascial trigger points. Physical Therapy, 80 (10), 997-1003.
Taunton, J. E., Ryan, M. B., Clement, D. B., McKenzie, D. C., Lloyd-Smith, D. R., and Zumbo, B. D. (2002). A retrospective case-control analysis of 2002 running injuries. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 36, 95-101.
Hong, J. H., and Kim J. S. (2013). Dignosis of iliotibial band friction syndrome and ultrasound guided steroid injection.The Korean Journal of Pain, 26 (4), 387-391.
Sangkaew, C. (2007). Surgical treatment of iliotibial band friction syndrome with the mesh technique. Archives of Orthopaesic and Trauma Surgery, 127, 303-306.