Improve Running Posture
Running posture is essentially how you hold your body while running…simple! When looking at the running posture of elite runners, there are quite a few similarities: they run tall, have a subtle forward lean while they are running, limit their up/down movement, and limit their side to side movement. Let’s take a look at each of these individually. *This post will focus on endurance running as the mechanics/posture change with other running events.*
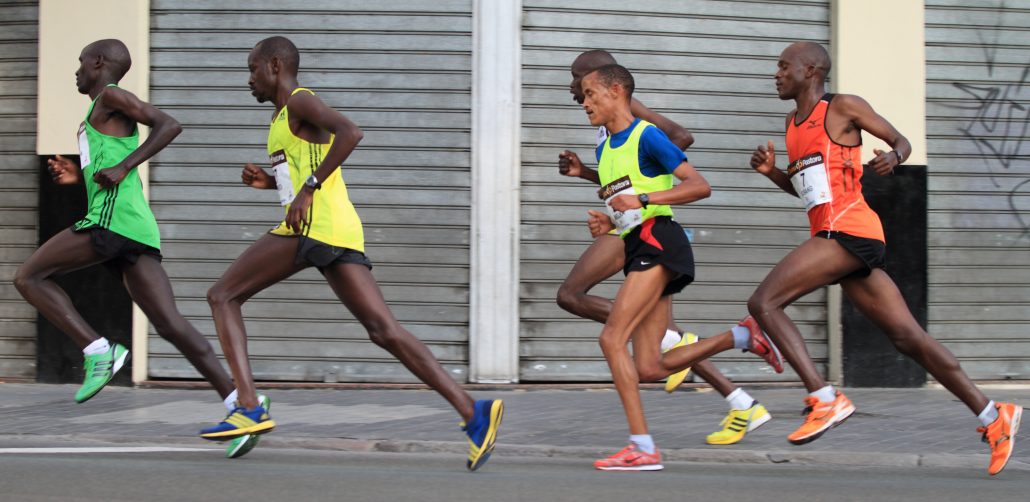

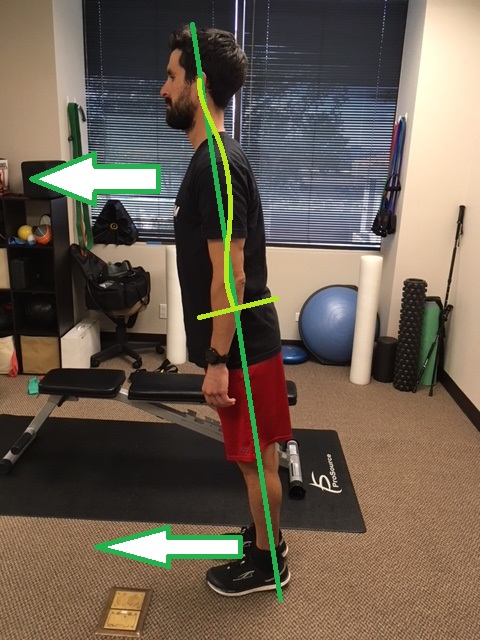
Run Tall
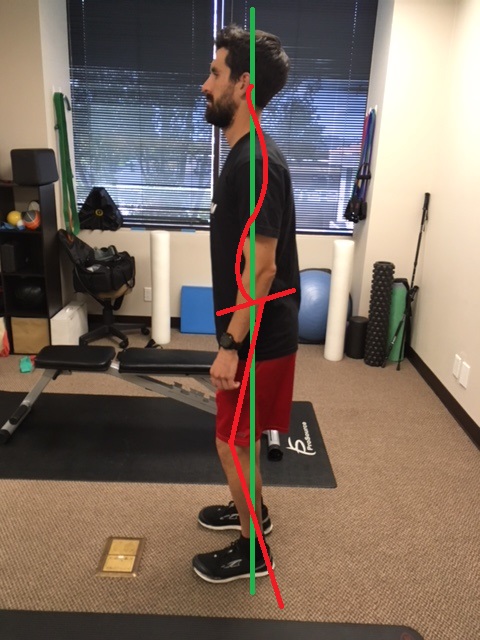
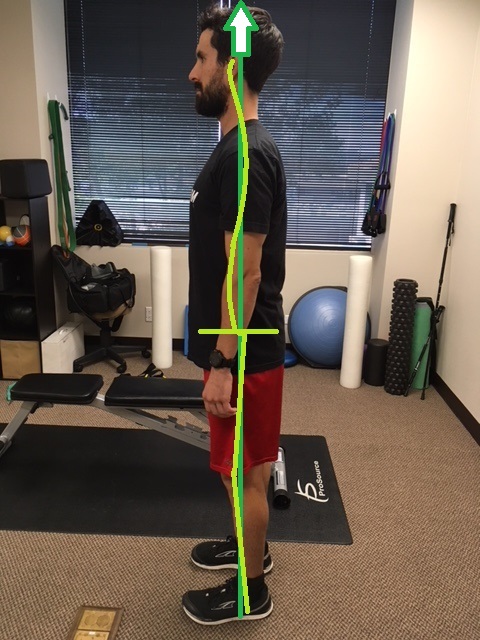
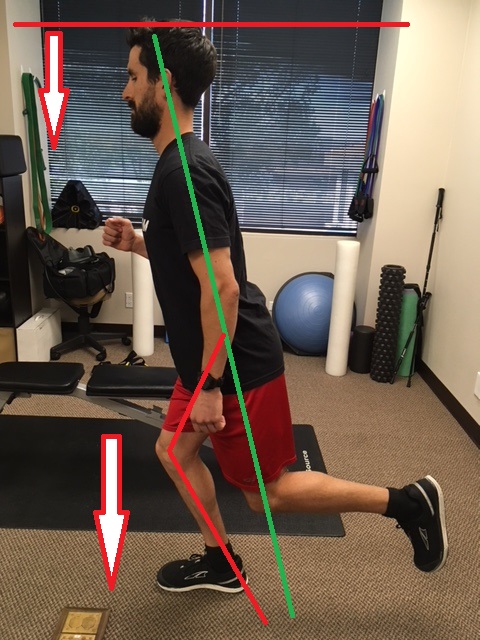
Let’s do a quick test…Stand up and relax your body, looking straight forward. Now, while looking straight forward, think about stretching through your body to each your head towards the ceiling. Another way to think of it is a rope is attached to your head and is pulling your body towards the ceiling. You should feel “taller” and more engaged with your muscles around your spine. This helps activate the spine stabilizing muscles to maintain proper posture: head over shoulders, shoulders over hips, hips over feet.
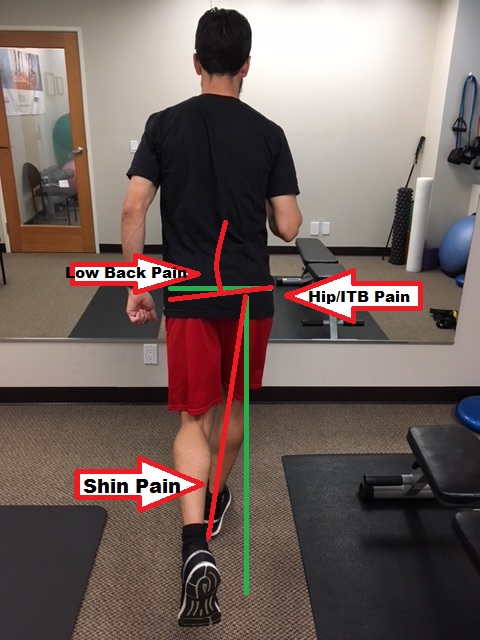
This spinal stiffness will help us run more efficient and help manage forces traveling through our muscles and joints much easier. In which picture does the runner appear ready to run?


Subtle Lean
Quick test number 2! Stand tall as described above. Now practice moving slightly forward and slightly backward through your ankles; the rest of your body is nice and straight. Good! Now slowly lean forward until you must move one of your legs to “catch” yourself from falling. Practice that a few times. The point where you need to move your leg is roughly where you want to hold yourself while running. This forward lean from the ankles, shifts your center of gravity ever so slightly forward to maintain momentum once you begin running. The faster you run, the more forward lean there is. ********Caution******** Avoid leaning from the waist! When reading about forward lean, runners think “Yea! Lean forward and get my momentum going!”. Leaning from the waist can potentially cause injury particularly at the back, and knees. Don’t do it!
Limit Up and Down Movement
When you think about it, running is a one legged sport; one foot touches the ground, then after a quick transition period of being fully in the air, the other foot touches the ground. This happens very quickly, step after step to keep the body moving forward. What is commonly seen as a runner runs by is a noticeable up and down bounce with their body; this IS a normal movement to an extent but causes issues when it is too great. Two main things frequently occur with beginner and intermediate runners when there is too much up and down movement: 1. There is too long of contact with the foot and the ground allowing the body to “sink” towards the ground due to increased bending at the hip, knee, and ankle, 2. A forceful push off from the toes pushes the body upward and forward.
Ever have extremely sore quads or calves (or both!) following a race? Soreness that lasts days? I have! Why are the legs so sore? When the leg is in contact with the ground for a longer time, the ankle, knee, and hip bend more while the muscles are contracting. This produces eccentric loading to the muscles (muscles lengthen while contracting) which causes the greatest amount of muscle damage. When does this occur? Late in races when our posture deteriorates, and our cadence slows down. Then we try to keep the pace up and muscle through the rest of the run with a slow cadence, resulting in a more forceful push off with our toes… now our calves hurt! Proper posture and a high cadence will help avoid this sequence from occurring or significantly limit the effects.
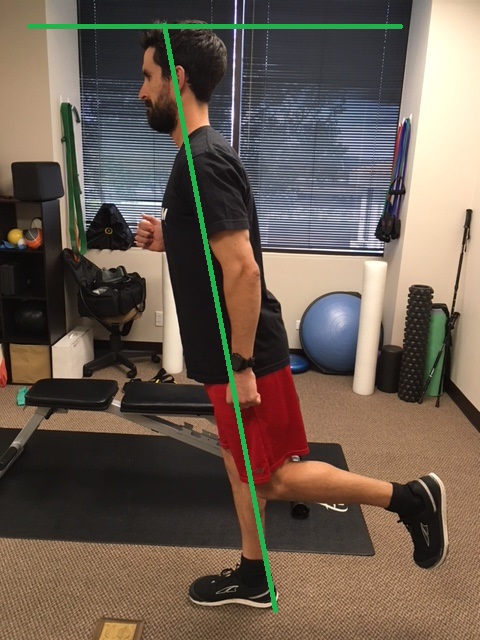

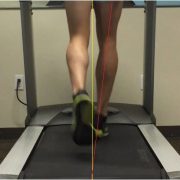
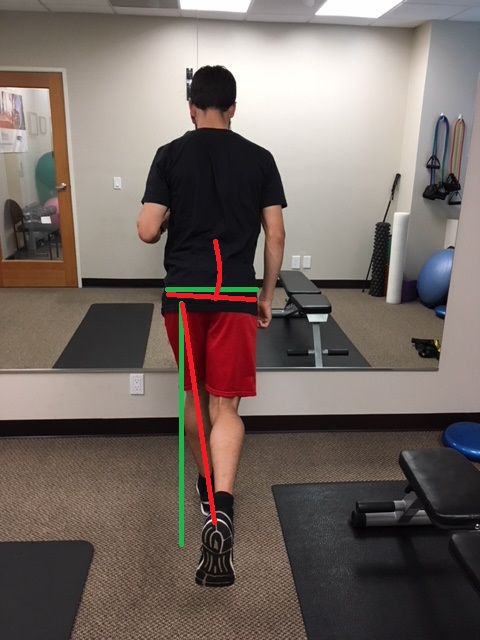
Limit Side to Side Movement
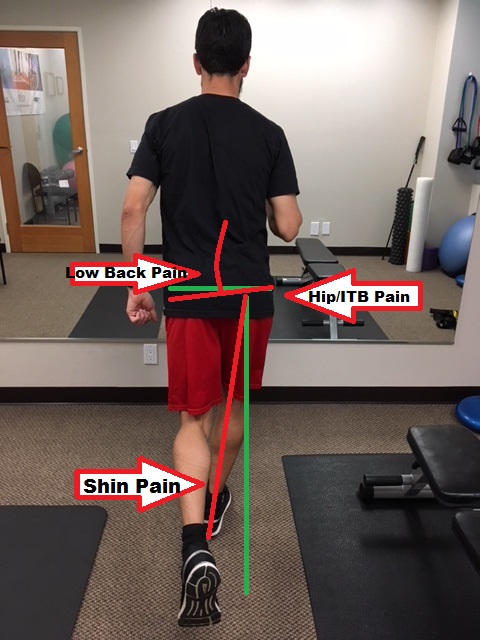
When running forward, we want our foot to land closer to our body, and under our hips. Similar to above, if there is too much contact time due to a slow cadence, the hip of the swing leg will drop. Now with the hip dropped down, the leg swings forward more towards mid line and then the foot lands, it is now mid line or has crossed over mid line, referred to as a “cross-over running gait” or “tight rope running”. This is the runner you see bounding side to side down the boardwalk. Do you do it? Ever hit your lower leg with your shoe, or see scuff marks on your calf after you run? Those are signs of hip drop; it changes the angle for your leg to move through and literally hits your stance leg. Read more about cross-over gait at our blog here.
Too much side to side movement will decrease your efficiency and set you up for potential injury. If your leg is crossing mid line, the inner muscles/tendons/foot are strained more; recurring posterior shin splints is a common ailment with this gait. There should be a small space between where your feet contact the ground. A strong runner may hide this for shorter runs but as fatigue sets in for longer runs, this will become more and more noticeable. Strength training, running more frequently, and specific drills will help avoid this.
Still with me? That wraps up running posture. Performing the following drills can help improve your running posture and prevent it from breaking down during long runs and races. Schedule with us at Peak Form Health Center to tailor specific exercises to your needs! We are conveniently located in Mission Valley, San Diego!
Tech
Lumo Run- At our Mission Valley office, we encourage our patients to purchase Lumo Run by Lumo tech. It is a wearable device that gives instant feedback (and post run feedback) on many running variables including all the posture points discussed above. Go to the lumobodytech website using this link Lumorun for $10 off! Check out our blog late April 2018 for a full Lumo Run review!
Drills
Posture and Lean
Walk with a Purpose– Stand tall as described above. With each step, push your leg back by squeezing your butt muscles. Continue reaching your head towards the ceiling while doing so. Most of the movement should come from the hip, not the lower back or by pushing off from the foot. Start by working on this before runs 1 minute at a time, but eventually incorporate into your normal walking!
Subtle lean– Stand tall. Rock back and forth from your ankles. 10 forward to help build awareness to where you should be leaning from.
Lean and step– Stand tall. Slowly lean forward until you have to take a step to “catch” yourself from falling forward. Helps work on maintaining a forward lean and proper timing of the first step. 10 steps each leg, three times through.
Band around waist- Anchor an elastic band around a fence, pole, tree, etc. and then place the band around the front of your hips. Walk until you feel the band start gently pulling you back. Now stand tall, keep your body inline and lean forward through your ankles against the band resistance. Move forward and backward to get a feel for a proper lean. Also, once you are leaning into the band, hold that position while taking slow steps in place.
Excessive Bounce
Up and down visualization– Run on a treadmill. Think about a water line right below your mouth; you have to stand tall to and avoid bouncing to avoid falling below that line or else you will be breathing in water. Alternatively, There is a low ceiling right above your head. You must keep your head still or else you will bang your head (Personally do not like this one as much because it does not reinforce elongating your spine/standing tall.)
Cadence– See our blog on cadence here. There are drills in detail there. The purpose is to increase cadence to decrease the amount of time your foot is on the ground so it does not “sink” down resulting in excessive up and down motion.
Cross over gait
Track line– Run around a track with lane lines (bicycle lane line on the road or other lines with similar width work). Run so the line is right in the middle of your body. Your INNER right foot should hit the right border of the line; your INNER left foot should hit the left border. This will force you to run with a wider stance to avoid side to side movement. Occasionally look down to see where your feet are or run with a partner running behind you to give you feedback.