Manage Triathlon Injuries and Training
Triathlon season is in full swing here in San Diego. With local races nearly every weekend, many triathletes have trouble balancing time between training, family, jobs, and racing competitively. Many triathletes begin to notice nagging triathlon injuries that are consistently getting worse as the season continues. Should they take a break to heal? Maybe. It depends on the athlete, their goals, and how they take care of their bodies during the season. Below are the top 5 triathlon injury management techniques we recommend to our athletes.

- Sports Chiropractic Care– We may be slightly biased here but this is the reason why we do what we do. We offer the best manual therapy and exercise methods to keep our triathletes swimming, biking and running. Triathlon injuries are managed effectively with a combination of Active Release Technique, Graston technique, joint manipulation and rehabilitative exercise. Have you seen or are you currently seeing a Sports Chiropractor? Sports chiropractic utilizes all the techniques previously mentioned as well advice on training through the injury; you can read more about the difference between a general chiropractor and a sports chiropractor here: Benefits of Sports Chiropractic.

- Maintain a Self Care Program– After being screened by a Sports Chiropractor and prescribed exercises, it is important that you do them! A daily routine of foam rolling, stretching, strengthening to the areas that have been causing injury. Daily is best but if you can squeeze in 3 times per week to manage triathlon injuries, you will see positive results.
- Sleep– It is important when training to stick to an appropriate sleep schedule. Getting quality sleep allows your body to regenerate after you break it down during hard training. In a nutshell, deep sleep allows growth hormone and other rebuilding hormones to be released which will allow you to bounce back faster. If sleep is constantly sacrificed for more work, or more training, the body will become catabolic and slowly break down. When trying to manage triathlon injuries, if you do not allow the body to rebuild, the injuries will never fully heal.
- Nutrition- Proper nutrition gives the building blocks to your body to allow for proper recovery. The more high quality fuel you give yourself, the high quality output and recovery you will get. Just like a sports car, you will not put regular unleaded gas in tank, you will put premium gas in to get the most out of the high performance engine. In general, high quality carbohydrate (lots of veggies, whole grains), lean proteins, and plenty of healthy fats are what you want to strive for! After exercise sessions, especially high intensity interval sessions, drink a mixture of carbohydrate and protein to refuel the glycogen stores in the muscles.

- Periodization- We see countless athletes in our office who suffer from over training syndrome. A lot of it stems from the fear of not doing enough to get ready for a race or losing too much fitness between exercise sessions. With a proper training plan in place, you will become fitter, faster, and having to manage triathlon injuries will become a thing of the past. In short, get an experienced coach, or at the very least get a training book and follow it.
Those are the top 5 tips to help manage triathlon injuries and avoid new injuries moving forward. We recommend getting a physical assessment by one of our sports chiropractors located in Mission Valley, San Diego. We are located near the neighborhoods of Hillcrest, Serra Mesa, Clairemont Mesa, La Mesa, Pacific Beach, Ocean Beach, and Point Loma. Our Sports Chiropractors are trained in musculoskeletal diagnosis and treatment, running gait analysis, bike fitting, and can order the proper diagnostic tests if necessary (MRI, X-ray, etc.).
Dr. Travis Rose, DC CCSP and Dr. Kevin Rose DC DACBSP are both avid triathletes and are passionate about helping triathletes manage triathlon injuries. Knowing first hand how frustrating a nagging injury can be, both Dr. Travis and Kevin utilize Active Release Treatments and chiropractic treatments to keep them healthy and performing at their best!



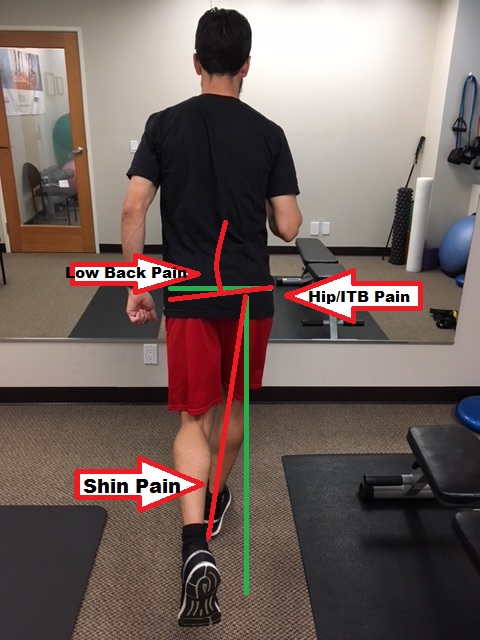













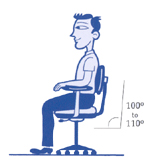
 In actuality, sitting with picture-perfect posture for long periods of time can actually lead to more discomfort, as it is extremely fatiguing. It can also lead to joint-pain and muscle strain because the torso is placing constant pressure on the lower disks in your back. Even in the ergonomically correct position, your arms and hands can still incur injuries. Any time you are sitting or standing in a static position, you increase the risk of prolonged physical conditions. To avoid any injuries at your workstation, try alternating between sitting and standing while working. Choose dynamic positions that will increase blood flow and alleviate stiff muscles. Also, include small rest breaks and stretch frequently to help avoid injuries.
In actuality, sitting with picture-perfect posture for long periods of time can actually lead to more discomfort, as it is extremely fatiguing. It can also lead to joint-pain and muscle strain because the torso is placing constant pressure on the lower disks in your back. Even in the ergonomically correct position, your arms and hands can still incur injuries. Any time you are sitting or standing in a static position, you increase the risk of prolonged physical conditions. To avoid any injuries at your workstation, try alternating between sitting and standing while working. Choose dynamic positions that will increase blood flow and alleviate stiff muscles. Also, include small rest breaks and stretch frequently to help avoid injuries.