Debunked Workstation Myths
There are many commonly accepted guidelines for a safe and comfortable workstation that are actually myths. Some postures and furniture can actually harm you and lead to discomfort, if rigidly followed. These debunked workstation myths will help you to manage the health risks of your home or work office:
Debunked Workstation Myths
Myth #1: Sitting correctly at a desk will eliminate discomfort and reduce injuries.
 In actuality, sitting with picture-perfect posture for long periods of time can actually lead to more discomfort, as it is extremely fatiguing. It can also lead to joint-pain and muscle strain because the torso is placing constant pressure on the lower disks in your back. Even in the ergonomically correct position, your arms and hands can still incur injuries. Any time you are sitting or standing in a static position, you increase the risk of prolonged physical conditions. To avoid any injuries at your workstation, try alternating between sitting and standing while working. Choose dynamic positions that will increase blood flow and alleviate stiff muscles. Also, include small rest breaks and stretch frequently to help avoid injuries.
In actuality, sitting with picture-perfect posture for long periods of time can actually lead to more discomfort, as it is extremely fatiguing. It can also lead to joint-pain and muscle strain because the torso is placing constant pressure on the lower disks in your back. Even in the ergonomically correct position, your arms and hands can still incur injuries. Any time you are sitting or standing in a static position, you increase the risk of prolonged physical conditions. To avoid any injuries at your workstation, try alternating between sitting and standing while working. Choose dynamic positions that will increase blood flow and alleviate stiff muscles. Also, include small rest breaks and stretch frequently to help avoid injuries.
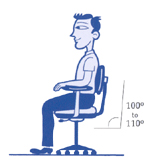
Myth #2: Always sit upright, and never recline at the workstation.
4 out of 5 workers would prefer to recline their chair slightly when working. In fact, a reclined position creates much less fatigue than sitting upright. Being slightly reclined is also much easier to maintain and alleviates gravitational pressure on the lower disks in the back. However, be cautious to avoid slouching, which can cause injuries from a lack of sufficient back support.
Myth #3: Ergonomic chairs are one-size fits all.
A single chair size won’t fit every shape and size. Women are shaped differently than men, and their hips are generally wider. Men usually have longer legs and consequently will need a deeper seat. There are many different body types, and each one requires a different seating solution. In addition, different chairs are appropriate for different tasks. When selecting an ergonomic chair, consider the tasks you will be doing and your body size and shape.
Myth #4: Adjust the chair height according to the table height.
Unfortunately, this is not always the case. Although it may seem like a simple solution, this does not always result in a safe sitting position. Instead, keep your chair at the appropriately adjusted position for your body type. If your chair is too low, it can add extra pressure to your legs and back. If the chair is set too high, it can result in discomfort from your feet dangling. You can get a footrest to avoid this, but the best way to avoid injuries is to adjust the table height or the task at hand.
Many people don’t realize that these commonly believed workstation postures are in fact myths. By educating yourself with the above recommendations, you can avoid unnecessary workstation injuries and added discomfort.



 The key to choosing the right chair is the ability to adjust the seat depth, height, and tilt. Choose a seat depth that supports your hips and legs, and look for a chair with sliding seat options. There should be a 1-2” space between the back of your knees and the front of the seat. The height of the chair needs to adjust according to your height. Your feet should be flat on the ground when your hips are pushed to the back of the seat, and you should be able to tilt the chair back to recline or sit upright. A reclining mechanism can also help with increasing movement while working.
The key to choosing the right chair is the ability to adjust the seat depth, height, and tilt. Choose a seat depth that supports your hips and legs, and look for a chair with sliding seat options. There should be a 1-2” space between the back of your knees and the front of the seat. The height of the chair needs to adjust according to your height. Your feet should be flat on the ground when your hips are pushed to the back of the seat, and you should be able to tilt the chair back to recline or sit upright. A reclining mechanism can also help with increasing movement while working.